AI-generated images are no longer a novelty – they’re now a powerful creative tool used by designers, marketers, and content creators alike. According to a 2024 report by Adobe, over 83% of digital professionals already use AI-generated visuals in their workflows, with adoption rising sharply across industries. ChatGPT plays a central role in this shift, thanks to its seamless integration with powerful image-generation models like DALL·E.
That said, ChatGPT itself doesn’t “draw” images in the traditional sense. Instead, it acts as a prompt engine and interface for models like DALL·E 3, which is built to turn descriptive language into high-quality visual outputs. The results depend entirely on how well the prompt is written – and how the model interprets it.
What ChatGPT Can Generate Visually
When connected to image generation tools, ChatGPT can guide the creation of:
- Realistic scenes like portraits, nature shots, or interiors
- Artistic illustrations in styles such as watercolor, anime, oil painting, or digital sketch
- Conceptual visuals used for moodboards, storytelling, or creative ideation
- Logo drafts or branding concepts based on descriptive input
Each image reflects the prompt’s clarity and detail. The better you describe the subject, atmosphere, composition, and style, the more useful the output becomes.
What ChatGPT Can’t (Fully) Do
Even with access to cutting-edge models, limitations still exist:
- Text inside images is often inaccurate or distorted. AI still struggles with clean typography or consistent lettering.
- Hyperrealism can be hit-or-miss. Faces and hands are common trouble spots, especially when prompts lack detail.
- Technical accuracy -like blueprints, charts, or precise product diagrams – typically requires post-editing or specialized tools.
- Multiple image generations at once aren’t currently supported inside ChatGPT itself – you generate and iterate one at a time.
Knowing these limits helps set realistic expectations and allows for smarter prompt planning and post-editing.
Setting Up ChatGPT for Image Generation
To get started with creating images through ChatGPT, you’ll need the right version, the right access, and the right setup. Here’s how to get everything ready without getting lost in menus or settings.
Accessing the Right Version of ChatGPT
Only specific versions of ChatGPT support image generation:
- ChatGPT Plus (GPT-4o): Required to access the integrated image generation powered by DALL·E 3.
- Available through the web app, iOS and Android apps, or desktop platforms with the ChatGPT interface.
- Free-tier users do not currently have access to native image generation. Upgrading to ChatGPT Plus is essential if you want built-in visuals.
You’ll know image tools are active when you see an “image” icon or “Generate image” option after entering a descriptive prompt.
Connecting to Image Generation Tools (DALL·E, Plugins, API)
Inside ChatGPT, image generation is powered directly by DALL·E 3, which doesn’t require separate signups or logins once you’re using the right version. Here’s how to activate and use it:
- Log into ChatGPT with a Plus account.
- Open a new chat and select GPT-4 or GPT-4o from the model switcher.
- Type a descriptive prompt like:
“A vintage bookstore interior at golden hour, realistic lighting, warm tones, cozy atmosphere” - The chat window will respond with a preview of the generated image. You can then ask for variations or changes directly.
- Click the image to open it in full view, then download or copy the file.
If you’re working outside the ChatGPT interface, such as through an app or API, OpenAI’s platform documentation explains how to access DALL·E directly through an endpoint or integration. Some tools also include third-party plugins or extensions that link ChatGPT to external image models – but for most users, the built-in DALL·E support is more than enough.
Writing Effective Prompts for Image Quality
Prompt writing is the single most important factor in generating high-quality AI images. The model only understands what it’s told – so clarity, specificity, and stylistic direction matter more than most users realize. Over 62% of designers using AI tools cite unclear prompts as the biggest barrier to useful results. The fix? Learn to speak the model’s language – descriptively, precisely, and with a creative lens.
Use Clear and Specific Descriptions
The AI responds to exactly what you give it – no more, no less. Vague inputs lead to generic, forgettable images. Strong prompts lay out the core elements of a visual idea: subject, style, environment, mood, and visual focus.
Here’s a comparison:
Weak prompt:
“Draw a person in a room”
Strong prompt:
“A young woman sitting by a large window reading a book, soft sunlight streaming in, cozy vintage room, muted earth tones”
The second prompt paints a scene. It gives the AI visual direction, mood, and texture—all crucial for meaningful output.
When crafting prompts, include:
- Subject clarity: who or what is the focus?
- Environment or setting: where is it happening?
- Style or tone: realistic, dreamy, dramatic?
- Color palette: muted, bold, monochrome?
- Perspective: close-up, aerial, wide shot?
These layers guide the model toward visuals that feel intentional rather than generic.
Incorporate Artistic Styles and Keywords
Stylistic references help guide the AI’s interpretation. Want something gritty and futuristic? Ask for “cyberpunk.” Need a logo that feels handcrafted? Try “watercolor” or “flat design.”
Some useful style-based terms:
- “Oil painting” – Adds texture and classic brush strokes
- “Isometric” – Creates 3D-like technical angles
- “Surrealist” – Great for dreamlike, abstract visuals
- “Cartoon-style” – Simplifies forms for bold, animated looks
- “Brutalist” – For stark, minimalist graphic compositions
- “Studio photography” – Ideal for product mockups or portraits
Try combining visual elements with a style tag:
Prompt Example:
“A futuristic city skyline at dusk, viewed from above, in the style of a cyberpunk digital painting, purple and neon blue lighting, dramatic shadows”
Stylistic cues narrow the creative scope, helping the model avoid randomness and deliver more relevant images.
Set Technical Parameters (Resolution, Aspect Ratio, Detail Level)
ChatGPT (through DALL·E) doesn’t currently allow full technical control like Midjourney or Stable Diffusion, but it does interpret technical terms if included in prompts.
Add size or framing cues like:
- Aspect ratio: “square format,” “vertical for Instagram Stories,” “16:9 horizontal layout”
- Detail level: “highly detailed,” “minimalist,” “sketch-like”
- Focus terms: “shallow depth of field,” “macro close-up,” “wide shot from above”
Examples:
Prompt 1:
“A clean top-down view of a minimalist workspace with laptop, coffee mug, and notebook, white background, flat lay, 1:1 aspect ratio”
Prompt 2:
“Majestic snow-capped mountains at sunrise, panoramic view, sharp details, golden hour lighting, ultra wide format”
Even without granular settings, these additions shape the framing and complexity of the result.
Refining and Iterating on AI-Generated Images
Perfect results rarely come on the first try. The real value lies in revising prompts and requesting variations – iterating based on what’s working and what isn’t.
Review and Adjust Prompt Details
If an image looks off, step back and assess:
- Is the subject vague or too general?
- Did you forget to specify lighting, mood, or style?
- Are colors clashing or the wrong palette?
Example Adjustment:
Original prompt: “A dog in a park”
Generated issue: Dog looks cartoonish and out of proportion
Improved prompt: “A realistic golden retriever playing with a ball in a sunlit park, green grass, warm color palette, natural lighting”
Adding realism and lighting fixed the issue.
Use Variations and Remix Features
ChatGPT with image generation (via DALL·E 3) allows:
- Creating variations of a generated image
- Asking for slight changes (e.g., “Make the lighting more dramatic” or “Use cooler tones”)
- Remixing based on the original idea, while adjusting tone or layout
Once an image is created, just say:
“Create three variations with the same subject but in different art styles: watercolor, digital painting, and minimalist flat design”
This builds a library of options quickly, ideal for creative exploration, client presentations, or A/B testing.
Best Practices for Generating Specific Types of Images
Different image categories demand different creative approaches. A detailed prompt that works well for a landscape may fall short when used to generate a product shot or a portrait. Each use case requires unique cues to guide the model effectively, and knowing how to steer the output makes the difference between an average image and a polished one worth using.
Portraits and Characters
AI-generated faces often fall apart when prompts are too broad. Facial features, expressions, and lighting all require careful guidance to avoid distorted results.
When generating character or portrait images:
- Specify age, ethnicity, expression, and attire. These details help the model create more grounded, human-like results.
- Include camera angle cues like “headshot,” “three-quarter view,” or “profile.”
- For more realism, mention lighting style—like “soft natural light,” “studio lighting,” or “backlit silhouette.”
- Add mood or emotion with phrasing like “warm, gentle smile” or “focused, intense gaze.”
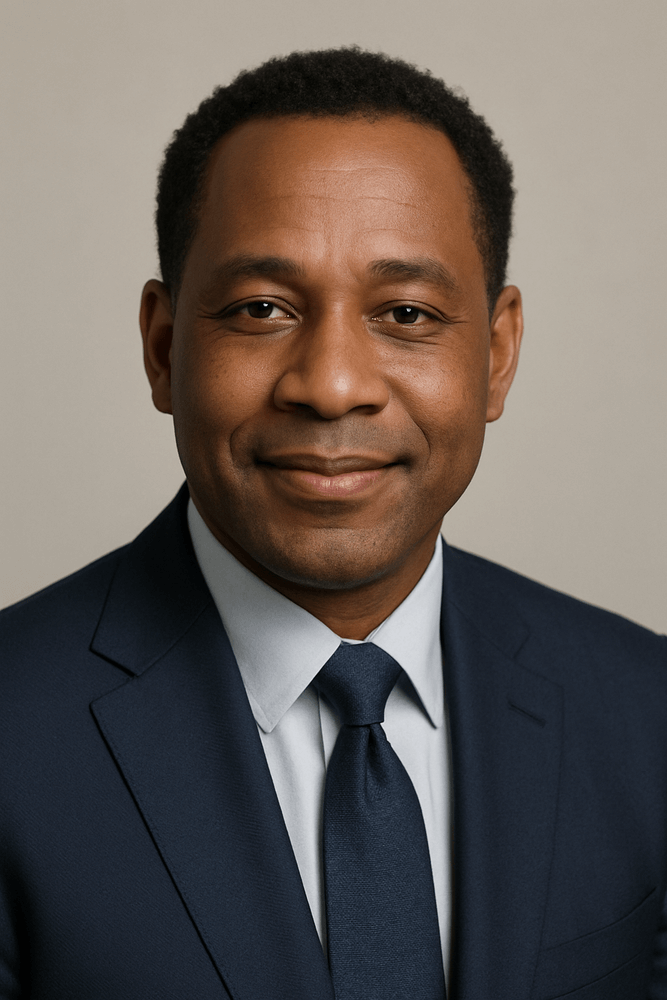
Prompt example:
“Portrait of a middle-aged Black man wearing a navy suit, soft smile, short curly hair, studio lighting, neutral background, head and shoulders composition”
Avoid using terms like “photo of a person” or “realistic man” without details, they often lead to generic or distorted faces.

Landscapes and Backgrounds
Landscapes are easier to generate cleanly, but the best results still depend on strong spatial and atmospheric language.
Key tips:
- Set the time of day: sunrise, golden hour, dusk, night.
- Choose a vantage point: aerial, wide angle, panoramic.
- Add seasonal or weather context: misty, snow-covered, sunlit, stormy.
- Mention geographic elements: rocky coastline, alpine forest, desert plateau.
Prompt example:
“Panoramic view of a snowy mountain range at sunrise, golden light hitting the peaks, blue and orange sky, pine trees in foreground, crisp winter atmosphere”
For background images, keep subjects minimal. A busy prompt can result in cluttered visuals.
Product Mockups and Graphics
Generating product visuals with ChatGPT + DALL·E works best when the prompt is framed like a product brief.
- State the object name and material: “matte black coffee tumbler,” “glass bottle with cork top”
- Add angle and perspective: “front-facing,” “45-degree angle,” “top-down flat lay”
- Mention environment only if needed: “placed on a wooden table,” or “floating against a white background”
- Use branding terms sparingly. Logos and text rarely render correctly—best added later in design tools.
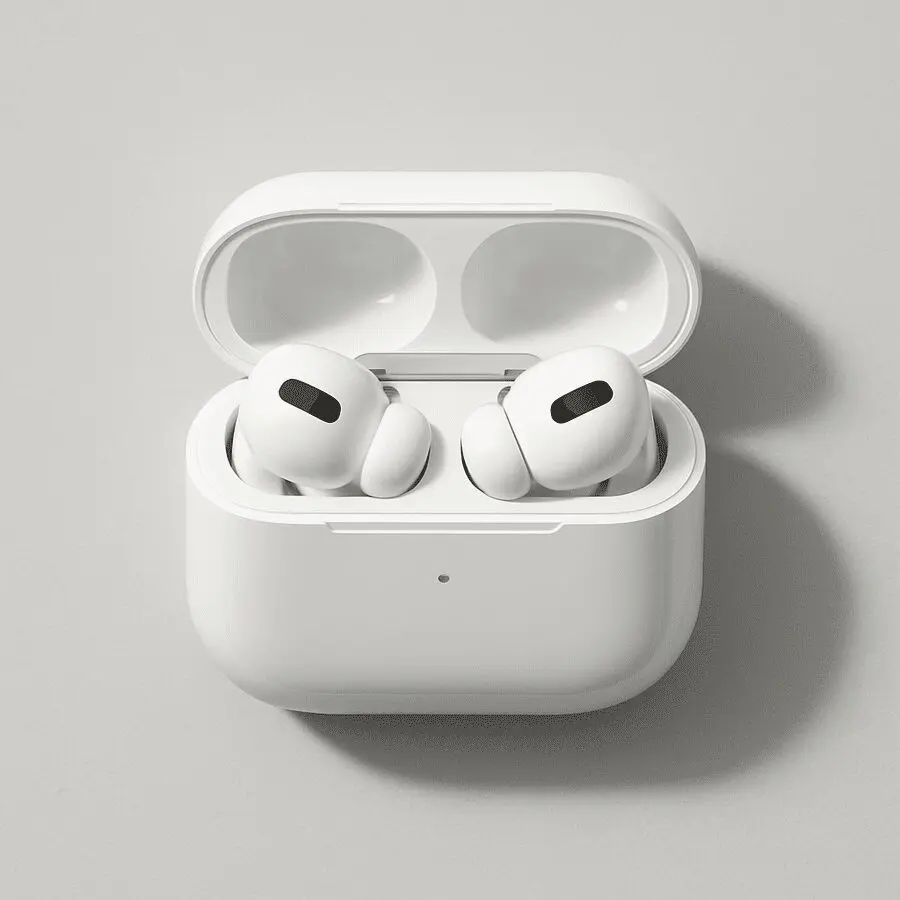
Prompt example:
“Top-down view of a white wireless earbud case with earbuds inside, sitting on a light gray surface, soft shadow, clean modern look”
Keep the focus tight. The more defined the product and setting, the better the composition.

Using ChatGPT to Create High-Quality AI Images (Step-by-Step)
One of ChatGPT’s most powerful creative use cases is helping users generate high-quality AI images without needing advanced design skills or technical prompt syntax. Rather than acting as a standalone image editor, ChatGPT works as a creative director and prompt optimizer, translating ideas into detailed instructions that image-generation models like DALL·E can understand clearly.
Turning Ideas Into Image-Ready Prompts
Most low-quality AI images stem from vague or incomplete prompts. ChatGPT eliminates this problem by helping you structure prompts the way image models “think.”
Instead of guessing what to type, you can explain your goal in plain language, for example:
“I need a modern hero image for a SaaS landing page that feels clean, trustworthy, and tech-focused.”
ChatGPT can then convert that request into a polished image prompt, such as:
“A clean, modern SaaS website hero image featuring abstract data flows and soft gradients, blue and white color palette, minimalist design, subtle lighting, professional tech aesthetic, wide horizontal layout.”
This translation layer is where image quality improves dramatically—because the prompt now includes style, mood, composition, and context, not just an object.
Improving Image Quality With Prompt Refinement
Once an image is generated, ChatGPT helps refine it systematically instead of relying on trial-and-error. You can describe what feels off, and ChatGPT will adjust the prompt accordingly.
Common refinement requests include:
-
Making the image look more realistic or more illustrative
-
Adjusting lighting, contrast, or color tone
-
Simplifying busy compositions
-
Changing perspective or framing
-
Matching a brand’s visual identity
Example:
“The image looks too dark and busy. Can you make it brighter and more minimalist?”
ChatGPT can respond with a revised prompt that removes unnecessary elements, adds lighting cues, and reinforces a clean visual style—often producing a noticeably better result in the next generation.
Creating Consistent Image Styles at Scale
For brands, consistency matters more than individual images. ChatGPT excels at helping maintain a repeatable visual style across multiple image generations.
You can ask ChatGPT to:
-
Define a reusable “style prompt” for your brand
-
Generate image prompts that follow the same color palette, lighting, and tone
-
Adapt one visual concept across multiple formats (blog, social, ads)
Example request:
“Create a reusable prompt style for minimalist SaaS illustrations we can use across our blog.”
This approach allows teams to generate dozens of visuals that feel cohesive—even when created over time or by different team members.
When ChatGPT Produces the Best Image Results
ChatGPT-driven image generation works especially well for:
-
Blog header images and featured visuals
-
Website sections and landing pages
-
Social media graphics and thumbnails
-
Concept art, moodboards, and ideation
-
Early-stage branding and visual exploration
While final production assets may still require light editing in tools like Canva or Photoshop, ChatGPT significantly reduces the time spent getting from idea to usable visual.
Why ChatGPT Improves Image Quality Overall
The biggest advantage isn’t the image model itself—it’s how clearly the idea is communicated. ChatGPT helps users:
-
Think visually
-
Clarify creative intent
-
Remove ambiguity from prompts
-
Iterate intelligently instead of randomly
As a result, the images generated are more aligned with the original goal, require fewer revisions, and feel intentionally designed rather than auto-generated.
Troubleshooting Common Image Generation Issues
Even with strong prompts, problems like visual artifacts, odd proportions, or mismatched styles can still show up. Most issues stem from vague phrasing or conflicting visual cues.
Fixing Unwanted Artifacts or Errors
Glitches – like extra limbs, blurry features, or broken symmetry – usually trace back to:
- Underspecified anatomy or structure (for humans or objects)
- Overly complex or abstract descriptions
- Conflicting modifiers (e.g., “flat design” and “hyperrealistic” together)
How to fix them:
- Remove contradictory or redundant words
- Break longer prompts into simpler, more focused sentences
- Add realism cues like “photo-real,” “balanced composition,” or “natural proportions”
Example correction:
Original: “A surreal fantasy dragon in a realistic jungle, high detail, graphic style, soft oil painting”
Revised: “A fantasy dragon perched on a tree branch in a realistic jungle, detailed scales, soft oil painting style, warm lighting”
Simplifying tone and clarifying structure often eliminates most errors.
Improving Realism or Style Consistency
Inconsistent results – like mismatched lighting, uneven color themes, or mixed artistic directions, usually come from missing style anchors.
To correct this:
- Choose one dominant style, and avoid mixing terms like “minimalist” and “hyperrealistic”
- Repeat core terms across variations to maintain visual cohesion
- Use modifiers like “cohesive palette,” “consistent lighting,” or “same perspective” when refining outputs
Prompt variation technique:
“Generate a variation of the previous image with the same composition and color palette but change the background to a beach scene”
Consistency doesn’t come from repetition, it comes from carefully controlled variety.
Ethical and Legal Considerations in AI Image Generation
AI-generated visuals open up powerful creative opportunities, but they also raise important questions about rights, fairness, and responsibility. Understanding what’s allowed, and what isn’t, is essential for using these tools safely and ethically.
Respecting Copyright and Usage Rights
Not all AI images are free from ownership concerns. Even though they’re generated algorithmically, some visuals may still be influenced by training data sourced from existing copyrighted works. That’s where things can get tricky.
Here’s what to keep in mind:
- Check the licensing terms of any platform you use. OpenAI, for example, grants full usage rights for images generated through ChatGPT, but not all platforms do the same.
- Avoid replicating known characters, logos, or branded visuals, especially for commercial use. Even if the model creates something “new,” it could still resemble protected content.
- For commercial projects (e.g., ads, packaging, merchandise), it’s safer to generate original compositions rather than referencing trademarked material.
Always verify whether commercial rights are included and stay updated on changing platform policies and regional copyright laws.
Avoiding Misuse or Misrepresentation
AI-generated images can mislead, offend, or harm, especially when used without proper context or disclosure. Responsible creators take steps to prevent misuse.
Avoid prompts that could result in:
- Deepfake-style outputs or images of real people in fabricated scenarios
- Distorted portrayals of vulnerable communities, cultures, or identities
- Images designed to deceive, like fake products or manipulated evidence
When sharing or publishing AI-generated images, especially in journalistic or educational contexts, include a brief note disclosing that the image was created with AI. Transparency builds trust, and protects against legal or reputational fallout.
How to Download, Edit, and Use Your AI Images
Once your image is ready, knowing how to handle the file matters just as much as the creative process.
Exporting Images in the Right Format
Different platforms and formats suit different outputs. Most AI image generators, including ChatGPT with DALL·E, offer download options in standard formats:
| Format | Best Use | Notes |
| PNG | Transparent backgrounds, logos, crisp visuals | Preserves quality, supports transparency |
| JPEG | Social posts, blog content, mobile use | Smaller file size, no transparency |
| WEBP | Web-optimized content | Modern compression, better loading speed |
| SVG | Icons, simple vector-like graphics | Only available via editing, not generated natively |
When in doubt, use PNG for quality or JPEG for smaller size.
Editing Images in External Tools (Canva, Photoshop)
AI visuals are a starting point, not always the final asset. Touching them up in design software helps tailor them for real-world use.
Common edits include:
- Adding text overlays with clean typography
- Inserting logos or brand colors manually
- Cropping or resizing to meet platform specs
- Color correction or retouching to match your visual tone
Canva works well for fast edits and social designs, while Photoshop gives deeper control over fine details and layer-based adjustments. We have a separate guide on how to use Canva for beginners.
Using Images for Web, Social, or Print
AI-generated images are highly versatile – but different formats demand different handling.
- For web and blog use, compress images (using TinyPNG or Squoosh) before uploading. It reduces load time without hurting visual quality.
- For social media, export in platform-optimized sizes (e.g., 1080×1080 for Instagram posts, 1200×630 for LinkedIn previews).
- For print, make sure the image is at least 300 DPI. If not, upscale it carefully using tools like Topaz Gigapixel or Adobe Firefly before finalizing.
Comparing ChatGPT Image Generation to Other AI Tools
With AI art tools evolving fast, it’s easy to get overwhelmed by the number of platforms out there. Each has its strengths. Some prioritize creative control. Others focus on accessibility. ChatGPT, integrated with DALL·E, stands out for its simplicity, but how does it compare to niche tools like Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, or Adobe Firefly?
Let’s break it down.
ChatGPT + DALL·E: Fast, Intuitive, and Conversational
ChatGPT isn’t a pure image-generation tool, it’s a conversational assistant with image capabilities. That gives it one major advantage: you don’t need to know prompt syntax or technical settings to get strong results.
Key advantages:
- No-code interface: You describe what you want, and it generates it—no prompt engineering skills needed.
- Seamless iteration: Ask for changes in plain English: “Make the lighting softer,” “Try it in a minimalist style,” etc.
- Integrated assistant: ChatGPT helps refine the prompt, not just execute it.
Best for:
- New users
- Quick creative drafts
- Broad-use cases like concept art, thumbnails, or mockups
Limitations:
- Less control over fine-grained details (e.g., seed numbers, depth maps)
- Currently lacks bulk generation or image upscaling features
Midjourney: High-End Creativity with a Steep Learning Curve
Midjourney is known for visually rich, stylized results—often used in creative industries for storyboarding, fashion concepts, or surreal art. But it’s not beginner-friendly.
Key features:
- Operates via Discord bot commands
- Generates four image options per prompt, each highly stylized
- Extensive community-created prompts and “prompt recipe” culture
Best for:
- Advanced users
- Artists seeking stylized or experimental visuals
- Moodboards or fantasy visuals
Trade-offs:
- Less intuitive
- Editing and refinement often require outside tools
- Limited realism for things like product shots or standard portraits
Stable Diffusion: Open-Source Flexibility, High Technical Control
Stable Diffusion appeals to power users and developers. It’s fully open-source, which means you can train custom models, fine-tune outputs, or deploy it locally—but none of that’s quick or simple.
Best for:
- Developers
- Brands needing control over data and models
- Technical teams building their own AI workflows
Downsides:
- Setup complexity
- Manual configuration for prompt parameters, resolution, and style consistency
Adobe Firefly: Designed for Designers
Firefly integrates directly with Adobe Creative Cloud, making it ideal for teams already using Photoshop, Illustrator, or Express.
Highlights:
- Commercial-use safe: trained on Adobe Stock, public domain, and open-license content
- Built-in editing pipeline: images can be sent directly to Adobe apps
- Focus on text effects, inpainting, and generative fills
Best for:
- Commercial teams
- Print, web, or brand design workflows
- Users who need safe, license-cleared content
Limitation:
- Still catching up in raw creative diversity compared to Midjourney
Tool Comparison Table
| Tool | Strength | Best For | Complexity |
| ChatGPT + DALL·E | Easy prompt refinement + fast results | Beginners, general creatives | ⭐ |
| Midjourney | Rich, stylized visuals | Artists, concept designers | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Stable Diffusion | Maximum customization | Developers, technical users | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Adobe Firefly | Commercial-safe content, integrations | Designers in Adobe ecosystem | ⭐⭐ |
Final Checklist: Getting the Best Images with ChatGPT
To wrap up, here’s a no-fluff checklist you can follow every time you generate visuals with ChatGPT:
- Start with a focused prompt
Mention subject, environment, mood, and perspective. - Add stylistic cues
Include terms like “digital painting,” “cyberpunk,” or “flat design” to guide style. - Set framing and format
Define aspect ratio, detail level, and image orientation. - Review, then iterate
Use plain language to ask for edits, tweaks, or new versions. - Watch for licensing needs
Use AI-generated visuals responsibly, especially for commercial projects. - Export in the right format
Choose PNG for quality, JPEG for speed, WEBP for the web. - Refine as needed
Polish final images using Canva, Photoshop, or your editing tool of choice.
Want this checklist in a handy reference sheet?
Explore BuzzCube’s design support services and ask us to create custom prompt templates tailored to your brand.



